Key Takeaways
Families play a crucial role in supporting a loved one’s recovery after a severe injury.
Understanding medical treatment, rehabilitation, and legal rights can help ease the transition.
Emotional and financial challenges can be overwhelming, but resources are available to help.
Learning how to provide care while maintaining personal well-being is essential.
A personal injury attorney can help secure compensation to cover medical costs, lost wages, and future care.
Introduction: The Impact of a Severe Injury on Families
When a loved one suffers a severe injury, it affects the entire family. Whether the injury is a spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury (TBI), amputation, or multiple fractures, the road to recovery can be long and uncertain. Family members often take on new responsibilities as caregivers, advocates, and financial planners. This sudden shift can be overwhelming, especially when balancing medical decisions, financial concerns, and emotional stress.
Understanding what to expect and how to access available support can help families navigate this challenging time. This guide provides an overview of medical care, rehabilitation, legal rights, and financial planning to help families support their loved ones effectively.
Step 1: Understanding the Medical and Rehabilitation Process
Severe injuries often require long-term medical care and rehabilitation. Family members should be involved in the treatment process to ensure their loved one receives the best care possible.
What to Expect During Initial Treatment
- Emergency care and hospitalization may last weeks or months, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Surgical procedures may be necessary to stabilize fractures, repair nerve damage, or reconstruct tissue.
- Intensive care may be required for individuals with traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord injuries.
The Role of Rehabilitation in Recovery
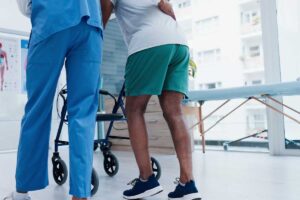
- Physical therapy helps regain strength and mobility.
- Occupational therapy focuses on relearning daily tasks like dressing and eating.
- Speech and cognitive therapy may be needed for brain injury survivors.
- Psychological support helps manage depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
How Families Can Support Rehabilitation
- Attend medical appointments and therapy sessions.
- Help with at-home exercises and mobility training.
- Learn about adaptive equipment and assistive devices.
- Encourage emotional support and maintain a positive outlook.
Step 2: Managing the Emotional Impact on the Family
Caring for an injured loved one can take an emotional toll on family members. It is important to recognize and address these challenges.
Common Emotional Responses
- Shock and grief over the sudden life changes.
- Anxiety about the future and financial stability.
- Feelings of helplessness or frustration.
- Depression and emotional exhaustion from caregiver stress.
Strategies for Coping
- Seek emotional support from counseling or support groups.
- Set realistic expectations for recovery and adaptation.
- Take breaks and practice self-care to prevent burnout.
- Encourage open communication among family members.
Step 3: Understanding Financial and Legal Considerations
A severe injury often leads to significant medical expenses and lost wages. Families should explore financial aid, insurance coverage, and legal compensation options.
Managing Medical Costs
- Review health insurance coverage for rehabilitation and long-term care.
- Apply for Medicaid or disability benefits if eligible.
- Seek charity and nonprofit assistance for uncovered expenses.
Exploring Legal Compensation Options
- If the injury was caused by negligence, a personal injury claim may provide compensation.
- Workers’ compensation may cover medical expenses if the injury occurred on the job.
- A lawsuit against responsible parties can help recover lost wages and future care costs.
Working With an Attorney
- An attorney can handle insurance disputes and legal claims.
- They can calculate damages to ensure the injured person receives adequate compensation.
- Legal representation can help secure financial stability for the future.
Step 4: Adjusting to Life as a Caregiver
Becoming a caregiver for an injured loved one comes with significant responsibilities. Learning how to provide care while maintaining personal well-being is crucial.
Daily Caregiving Tasks
- Assisting with bathing, dressing, and personal hygiene.
- Managing medications and therapy exercises.
- Helping with mobility, transportation, and household tasks.
- Monitoring for signs of complications or medical issues.
Avoiding Caregiver Burnout
- Ask for help from family, friends, or professional caregivers.
- Use respite care services for temporary relief.
- Maintain healthy habits, sleep, and mental health support.
- Join caregiver support groups for shared experiences and advice.
Step 5: Planning for Long-Term Support and Independence
As recovery progresses, families should plan for long-term care needs and independence goals.
Exploring Long-Term Care Options
- Home modifications for wheelchair accessibility, ramps, and adaptive equipment.
- Assisted living facilities for those requiring 24/7 care.
- Community resources, such as transportation services and meal delivery.
Encouraging Independence and Quality of Life
- Support engagement in adaptive sports, hobbies, or vocational training.
- Encourage social interactions and participation in community activities.
- Help set realistic goals for work, school, or independent living.
Conclusion: Providing Strength and Support for Recovery
A severe injury impacts not just the injured person but the entire family. By understanding medical care, financial assistance, and emotional well-being, families can play a critical role in their loved one’s recovery.